Page 86 - Math Course 2 (Book 1)
P. 86
Introduction to Polynomials
Mo. 3
Lesson 4
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. Identify and classify polynomials. Let’s Begin
2. Find the degree of a polynomial
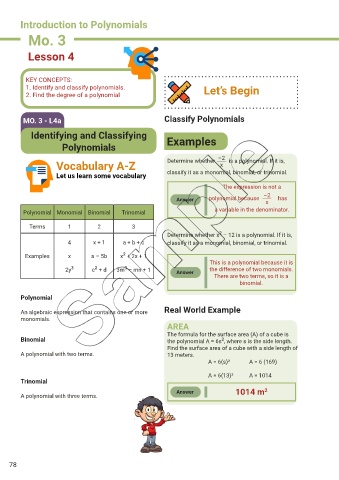
MO. 3 - L4a Classify Polynomials
Identifying and Classifying Examples
Polynomials
–2 is a polynomial. If it is,
Determine whether
Vocabulary A-Z x
Let us learn some vocabulary classify it as a monomial, binomial, or trinomial.
The expression is not a
–2
Answer polynomial because x has
a variable in the denominator.
Polynomial Monomial Binomial Trinomial
Terms 1 2 3
2
Determine whether x – 12 is a polynomial. If it is,
4 x + 1 a + b + c classify it as a monomial, binomial, or trinomial.
2
Examples x a – 5b x + 2x + 1
This is a polynomial because it is
3
2
2y 3 c + d 3m – mn + 1 Answer the difference of two monomials.
There are two terms, so it is a
binomial.
Polynomial
An algebraic expression that contains one or more Real World Example
monomials.
AREA
The formula for the surface area (A) of a cube is
Binomial the polynomial A = 6s , where s is the side length.
2
Find the surface area of a cube with a side length of
A polynomial with two terms. 13 meters.
A = 6(s)² A = 6 (169)
A = 6(13)² A = 1014
Trinomial
Answer 1014 m 2
A polynomial with three terms.
78