Page 86 - Science Course 2 (Book 1)
P. 86
Mo3-L3c: Why is Sexual Reproduction Important?
Key Concept
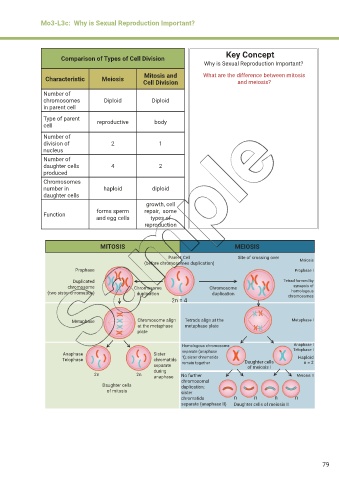
Comparison of Types of Cell Division
Why is Sexual Reproduction Important?
Mitosis and What are the difference between mitosis
Characteristic Meiosis
Cell Division and meiosis?
Number of
chromosomes Diploid Diploid
in parent cell
Type of parent reproductive body
cell
Number of
division of 2 1
nucleus
Number of
daughter cells 4 2
produced
Chromosomes
number in haploid diploid
daughter cells
growth, cell
forms sperm repair, some
Function
and egg cells types of
reproduction
MITOSIS MEIOSIS
Parent Cell Site of crossing over
(before chromosomes duplication) Meiosis
Prophase Prophase I
Duplicated Tetrad formed by
chromosome Chromosome Chromosome synapsis of
homologous
(two sister chromatids) duplication duplication chromosomes
2n = 4
Metaphase Chromosome align Tetrads align at the Metaphase I
at the metaphase metaphase plate
plate
Homologous chromosome Anaphase I
Anaphase Sister separate (anaphase Telophase I
Telophase chromatids 1); sister chromatids Daughter cells Haploid
n = 2
separate remain together of meiosis I
during
2n 2n anaphase No further Meiosis II
chromosomal
Daughter cells duplication;
of mitosis sister
chromatids n n n n
separate (anaphase II) Daughter cells of meiosis II
79