Page 127 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 127
Direct Variation Equation
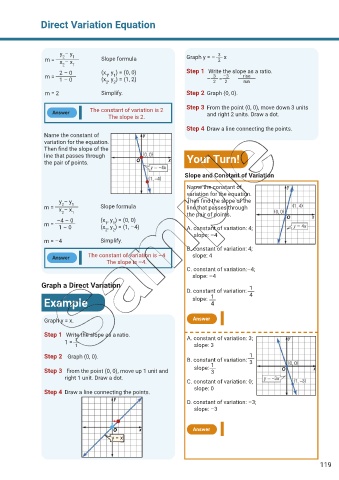
y – y 3
2
m = x – x 1 Slope formula Graph y = – x
2
2 1
2 – 0 (x , y ) = (0, 0) Step 1 Write the slope as a ratio.
1
m = 1 – 0 (x , y ) = (1, 2) – = rise
1
–3
3
run
2
2
2
2
m = 2 Simplify. Step 2 Graph (0, 0).
Answer The constant of variation is 2 Step 3 From the point (0, 0), move down 3 units
and right 2 units. Draw a dot.
The slope is 2.
Step 4 Draw a line connecting the points.
Name the constant of
variation for the equation.
Then find the slope of the
line that passes through Your Turn!
the pair of points.
Slope and Constant of Variation
Name the constant of
variation for the equation.
y – y Then find the slope of the
2
m = x – x 1 Slope formula line that passes through
2 1 the pair of points.
–4 – 0 (x , y ) = (0, 0)
1
1
m = 1 – 0 (x , y ) = (1, –4) A. constant of variation: 4;
2
2
slope: –4
m = –4 Simplify.
B. constant of variation: 4;
The constant of variation is –4 slope: 4
Answer
The slope is –4.
C. constant of variation:–4;
slope: –4
Graph a Direct Variation 1
D. constant of variation:
4
Example slope: 1
4
Graph y = x. Answer
Step 1 Write the slope as a ratio. A. constant of variation: 3;
1 = 1 slope: 3
1
1
Step 2 Graph (0, 0). B. constant of variation:
3
Step 3 From the point (0, 0), move up 1 unit and slope: 1
3
right 1 unit. Draw a dot.
C. constant of variation: 0;
slope: 0
Step 4 Draw a line connecting the points.
D. constant of variation: –3;
slope: –3
Answer
y = x
119