Page 52 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 52
Quadratic Equations: Graphing
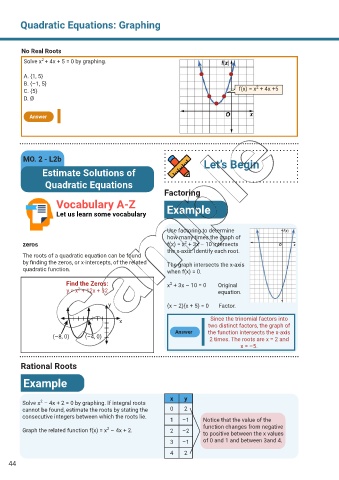
No Real Roots
2
Solve x + 4x + 5 = 0 by graphing.
A. {1, 5}
B. {–1, 5}
2
C. {5} f(x) = x + 4x +5
D. Ø
Answer
MO. 2 - L2b Let’s Begin
Estimate Solutions of
Quadratic Equations
Factoring
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary Example
Use factoring to determine
how many times the graph of
2
zeros f(x) = x + 3x – 10 intersects
the x-axis. Identify each root.
The roots of a quadratic equation can be found
by finding the zeros, or x-intercepts, of the related The graph intersects the x-axis
quadratic function. when f(x) = 0.
Find the Zeros: x + 3x – 10 = 0 Original
2
2
y = x + 12x + 32 equation.
y (x – 2)(x + 5) = 0 Factor.
x Since the trinomial factors into
two distinct factors, the graph of
Answer the function intersects the x-axis
(–8, 0) (–4, 0) 2 times. The roots are x = 2 and
x = –5.
Rational Roots
Example
x y
Solve x – 4x + 2 = 0 by graphing. If integral roots
2
cannot be found, estimate the roots by stating the 0 2
consecutive integers between which the roots lie.
1 –1 Notice that the value of the
function changes from negative
2
Graph the related function f(x) = x – 4x + 2. 2 –2 to positive between the x values
3 –1 of 0 and 1 and between 3and 4.
4 2
44