Page 50 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 50
Quadratic Equations: Graphing
Mo. 2
Lesson 2 Let’s Begin
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. Solve quadratic equations by graphing. Two Roots
2. Estimate solutions of quadratic equations
by graphing.
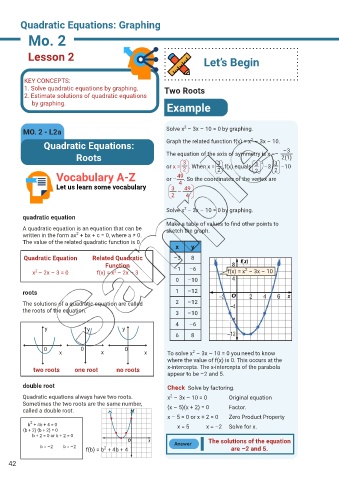
Example
2
MO. 2 - L2a Solve x – 3x – 10 = 0 by graphing.
2
Quadratic Equations: Graph the related function f(x) = x – 3x – 10. –3
Roots The equation of the axis of symmetry is x =– 2(1)
3
3
3
2
3
or x = . When x = ,f(x) equals –3 –10
2
2
2
2
Vocabulary A-Z or – . So the coordinates of the vertex are
49
Let us learn some vocabulary 3 4 49
–
2 4
Solve x – 3x – 10 = 0 by graphing.
2
quadratic equation
Make a table of values to find other points to
A quadratic equation is an equation that can be sketch the graph.
2
written in the form ax + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0.
The value of the related quadratic function is 0.
x y
Quadratic Equation Related Quadratic –3 8
Function
2
2
2
x – 2x – 3 = 0 f(x) = x – 2x – 3 –1 –6 f(x) = x – 3x – 10
0 –10
roots 1 –12
The solutions of a quadratic equation are called 2 –12
the roots of the equation. 3 –10
4 –6
y y y
6 8
0 0 0
x x x To solve x – 3x – 10 = 0 you need to know
2
where the value of f(x) is 0. This occurs at the
two roots one root no roots x-intercepts. The x-intercepts of the parabola
appear to be –2 and 5.
double root Check Solve by factoring.
Quadratic equations always have two roots. x – 3x – 10 = 0 Original equation
2
Sometimes the two roots are the same number,
called a double root. (x – 5)(x + 2) = 0 Factor.
x – 5 = 0 or x + 2 = 0 Zero Product Property
2
b + 4b + 4 = 0 x = 5 x = –2 Solve for x.
(b + 2) (b + 2) = 0
b + 2 = 0 or b + 2 = 0
Answer The solutions of the equation
b = –2 b = –2 2
f(b) = b + 4b + 4 are –2 and 5.
42