Page 76 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 76
Quadratic and Cubic Equations
Mo. 2
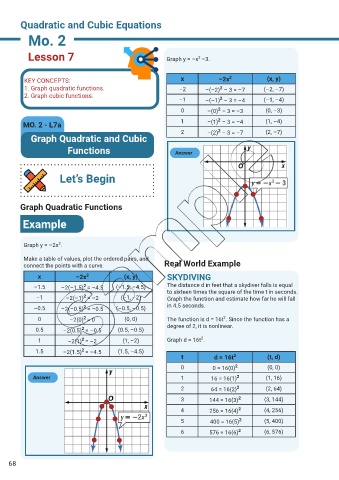
Lesson 7 Graph y = –x –3.
2
KEY CONCEPTS: x –2x 2 (x, y)
1. Graph quadratic functions. –2 –(–2) – 3 = –7 (–2, –7)
2
2. Graph cubic functions.
2
–1 –(–1) – 3 = –4 (–1, –4)
2
0 –(0) – 3 = –3 (0, –3)
2
MO. 2 - L7a 1 –(1) – 3 = –4 (1, –4)
2
2 –(2) – 3 = –7 (2, –7)
Graph Quadratic and Cubic
Functions Answer
Let’s Begin
Graph Quadratic Functions
Example
2
Graph y = –2x .
Make a table of values, plot the ordered pairs, and
connect the points with a curve. Real World Example
x –2x 2 (x, y) SKYDIVING
2
–1.5 –2(–1.5) = –4.5 (–1.5, –4.5) The distance d in feet that a skydiver falls is equal
to sixteen times the square of the time t in seconds.
2
–1 –2(–1) = –2 (–1, –2) Graph the function and estimate how far he will fall
2
–0.5 –2(–0.5) = –0.5 (–0.5, –0.5) in 4.5 seconds.
2
0 –2(0) = 0 (0, 0) The function is d = 16t . Since the function has a
2
degree of 2, it is nonlinear.
2
0.5 –2(0.5) = –0.5 (0.5, –0.5)
2
2
1 –2(1) = –2 (1, –2) Graph d = 16t .
2
1.5 –2(1.5) = –4.5 (1.5, –4.5)
t d = 16t 2 (t, d)
0 0 = 16(0) 2 (0, 0)
Answer 1 16 = 16(1) 2 (1, 16)
2 64 = 16(2) 2 (2, 64)
3 144 = 16(3) 2 (3, 144)
4 256 = 16(4) 2 (4, 256)
5 400 = 16(5) 2 (5, 400)
6 576 = 16(6) 2 (6, 576)
68