Page 50 - Science Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 50
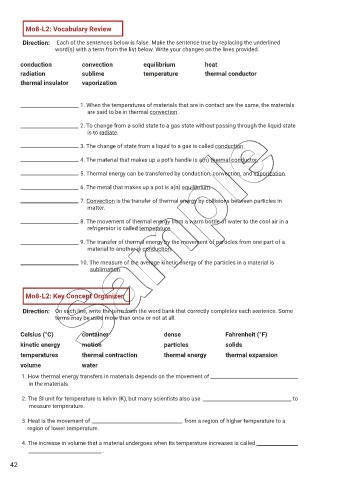
Mo8-L2: Vocabulary Review
Direction: Each of the sentences below is false. Make the sentence true by replacing the underlined
word(s) with a term from the list below. Write your changes on the lines provided.
conduction convection equilibrium heat
radiation sublime temperature thermal conductor
thermal insulator vaporization
1. When the temperatures of materials that are in contact are the same, the materials
are said to be in thermal convection.
2. To change from a solid state to a gas state without passing through the liquid state
is to radiate.
3. The change of state from a liquid to a gas is called conduction.
4. The material that makes up a pot’s handle is a(n) thermal conductor.
5. Thermal energy can be transferred by conduction, convection, and vaporization.
6. The metal that makes up a pot is a(n) equilibrium.
7. Convection is the transfer of thermal energy by collisions between particles in
matter.
8. The movement of thermal energy from a warm bottle of water to the cool air in a
refrigerator is called temperature.
9. The transfer of thermal energy by the movement of particles from one part of a
material to another is conduction.
10. The measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a material is
sublimation.
Mo8-L2: Key Concept Organizer
Direction: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some
terms may be used more than once or not at all.
Celsius (°C) container dense Fahrenheit (°F)
kinetic energy motion particles solids
temperatures thermal contraction thermal energy thermal expansion
volume water
1. How thermal energy transfers in materials depends on the movement of
in the materials.
2. The SI unit for temperature is kelvin (K), but many scientists also use to
measure temperature.
3. Heat is the movement of from a region of higher temperature to a
region of lower temperature.
4. The increase in volume that a material undergoes when its temperature increases is called
.
42