Page 53 - Science Course 2 (Book 1)
P. 53
Mo2-L3c: How Does the Body Protect Itself From Harmful Invaders?
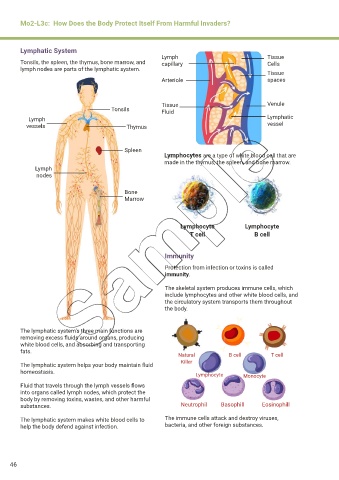
Lymphatic System
Lymph Tissue
Tonsils, the spleen, the thymus, bone marrow, and capillary Cells
lymph nodes are parts of the lymphatic system.
Tissue
Arteriole spaces
Tissue Venule
Tonsils Fluid
Lymph Lymphatic
vessels Thymus vessel
Spleen
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that are
made in the thymus, the spleen, and bone marrow.
Lymph
nodes
Bone
Marrow
Lymphocyte Lymphocyte
T cell B cell
Immunity
Protection from infection or toxins is called
immunity.
The skeletal system produces immune cells, which
include lymphocytes and other white blood cells, and
the circulatory system transports them throughout
the body.
The lymphatic system’s three main functions are
removing excess fluids around organs, producing
white blood cells, and absorbing and transporting
fats.
Natural B cell T cell
Killer
The lymphatic system helps your body maintain fluid
homeostasis.
Lymphocyte Monocyte
Fluid that travels through the lymph vessels flows
into organs called lymph nodes, which protect the
body by removing toxins, wastes, and other harmful
substances. Neutrophil Basophill Eosinophill
The lymphatic system makes white blood cells to The immune cells attack and destroy viruses,
help the body defend against infection. bacteria, and other foreign substances.
46