Page 120 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 120
Linear Equations: Rate of Change
Mo. 4
Lesson 1
Let’s Begin
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. Use rate of change to solve problems.
2. Find the slope of a line. Real World Example
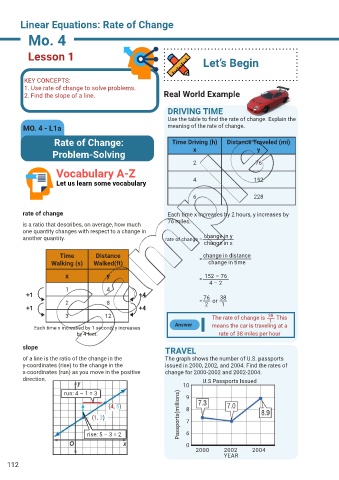
DRIVING TIME
Use the table to find the rate of change. Explain the
MO. 4 - L1a meaning of the rate of change.
Rate of Change: Time Driving (h) Distance Traveled (mi)
Problem-Solving x y
2 76
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary 4 152
6 228
rate of change Each time x increases by 2 hours, y increases by
76 miles.
is a ratio that describes, on average, how much
one quantity changes with respect to a change in
another quantity. rate of change = change in y
change in x
Time Distance = change in distance
Walking (s) Walked(ft) change in time
x y = 152 – 76
4 – 2
1 4
+1 +4 76 38
2 8 = 2 or 1
+1 +4
38
3 12 The rate of change is This
1
Each time x increased by 1 second, y increases Answer means the car is traveling at a
by 4 feet. rate of 38 miles per hour
slope
TRAVEL
of a line is the ratio of the change in the The graph shows the number of U.S. passports
y-coordinates (rise) to the change in the issued in 2000, 2002, and 2004. Find the rates of
x-coordinates (run) as you move in the positive change for 2000-2002 and 2002-2004.
direction. U.S Passports Issued
10
run: 4 – 1 = 3 9
(4, 5) 8
(1, 3) Passports(millions) 7
rise: 5 – 3 = 2 6
0
2000 2002 2004
YEAR
112