Page 131 - Math Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 131
Area: Triangles, Rhombi, And Trapezoids
Mo. 10
Lesson 5
Let’s Begin
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. Find areas of triangles. Areas of Triangles
2. Find areas of trapezoids.
3. Find areas rhombi.
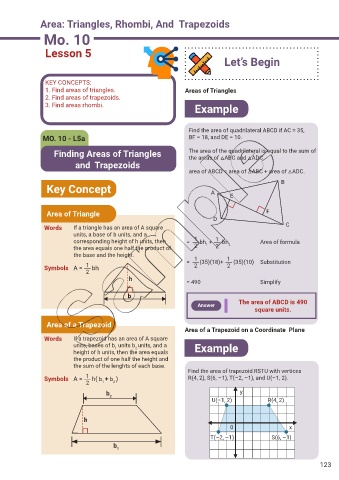
Example
Find the area of quadrilateral ABCD if AC = 35,
MO. 10 - L5a BF = 18, and DE = 10.
Finding Areas of Triangles The area of the quadrilateral is equal to the sum of
the areas of △ABC and △ADC
and Trapezoids
area of ABCD = area of △ABC + area of △ADC.
B
Key Concept A
E
Area of Triangle F
D
C
Words If a triangle has an area of A square
units, a base of b units, and a
1
1
corresponding height of h units, then = bh + bh Area of formula
2
1
the area equals one half the product of 2 2
the base and the height. 1 1
= (35)(18)+ (35)(10) Substitution
1
Symbols A = bh 2 2
2
h
= 490 Simplify
b
The area of ABCD is 490
Answer
square units.
Area of a Trapezoid
Area of a Trapezoid on a Coordinate Plane
Words If a trapezoid has an area of A square
units, bases of b units b units, and a Example
1
2
height of h units, then the area equals
the product of one half the height and
the sum of the lenghts of each base.
Find the area of trapezoid RSTU with vertices
1
Symbols A = h( b + b ) R(4, 2), S(6, –1), T(–2, –1), and U(–1, 2).
2 1 2
b 2 y
U(–1, 2) R(4, 2)
h
0 x
T(–2, –1) S(6, –1)
b
1
123