Page 132 - Math Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 132
Area: Triangles, Rhombi, And Trapezoids
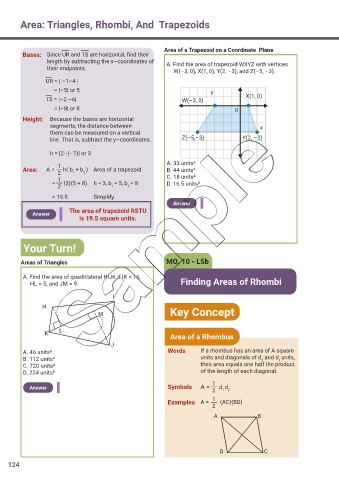
Area of a Trapezoid on a Coordinate Plane
Bases: Since UR and TS are horizontal, f nd their
length by subtracting the x–coordinates of A. Find the area of trapezoid WXYZ with vertices
their endpoints.
W(–3, 0), X(1, 0), Y(2, –3), and Z(–5, –3).
UR = | –1–4 |
= |–5| or 5 y
TS = |–2 –6| W(–3, 0) X(1, 0)
= |–8| or 8 0
Height: Because the bases are horizontal
segments, the distance between x
them can be measured on a vertical
line. That is, subtract the y–coordinates. Z(–5,–3) Y(2, –3)
h = |2–(–1)| or 3
1 A. 33 units²
Area: A = h( b + b ) Area of a trapezoid B. 44 units²
2 1 2
1 C. 18 units²
= (3)(5 + 8) h = 3, b = 5, b = 8 D. 16.5 units²
2 1 2
= 19.5 Simplify.
Answer
The area of trapezoid RSTU
Answer
is 19.5 square units.
Your Turn!
Areas of Triangles MO. 10 - L5b
A. Find the area of quadrilateral HIJK if IK = 16,
HL = 5, and JM = 9. Finding Areas of Rhombi
I
H
M Key Concept
L
K
Area of a Rhombus
J
A. 46 units² Words If a rhombus has an area of A square
B. 112 units² units and diagonals of d and d units,
1
2
C. 720 units² then area equals one half the product
D. 224 units² of the length of each diagonal.
1
Answer Symbols A = d d
2 1 2
1
Examples A = (AC)(BD)
2
A B
D C
124